MATERIALS
-Hot plate
-1 slide
-1 coverslip
-Tongs
-Needle
-Gram stain (crystal violet, iodine and safranin)
-Ethanol
-Microscope
-Yogurt
PROCEDURE
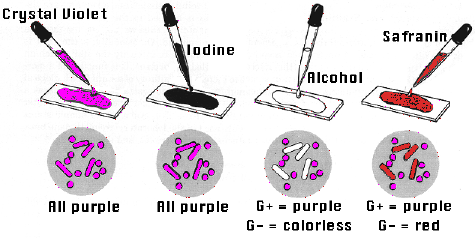
1- First we prepared a heat fixed sample of the bacteria by spreading somre yogurt on a slide and drying it on the hot plate.
2-Then we covered the smear with crystal violet and waited for 1 min. After that we rinsed it with distilled water.
3-We applied iodine solution for another 1 min and again rinsed it with distilled water.
4-Then we decolorized using ethaol. Drop by drop until the purple stops flowing and washed immediately with distilled water.
5-Lastly we covered the sample with safranin stain for and exposure time of 45 seconds and rinsed the sample with tap water.
6-Finally we dried the under part of the slide with paper and viewed it on the microscope.
Results and observations: We saw some bacteria red and other purple. Why?
Gram Positive Cell Wall:
Gram-positive bacteria have a thick
cell wall which is made up of peptidoglycan (50-90% of cell
wall), which stains purple. Peptidoglycan is mainly a polysaccharide
composed of two subunits. The thick
peptidoglycan layer of Gram-positive organisms allows these organisms to
retain the crystal violet-iodine complex and stains the cells as
purple.
Gram Negative Cell Wall:
Gram-negative bacteria have a thinner
layer of peptidoglycan (10% of the cell wall) and lose the crystal
violet-iodine complex during decolorization with the alcohol rinse, but
retain the counter stain Safranin, thus appearing reddish or pink. They
also have an additional outer membrane which contains lipids, which is
separated from the cell wall by means of periplasmic space.




No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario